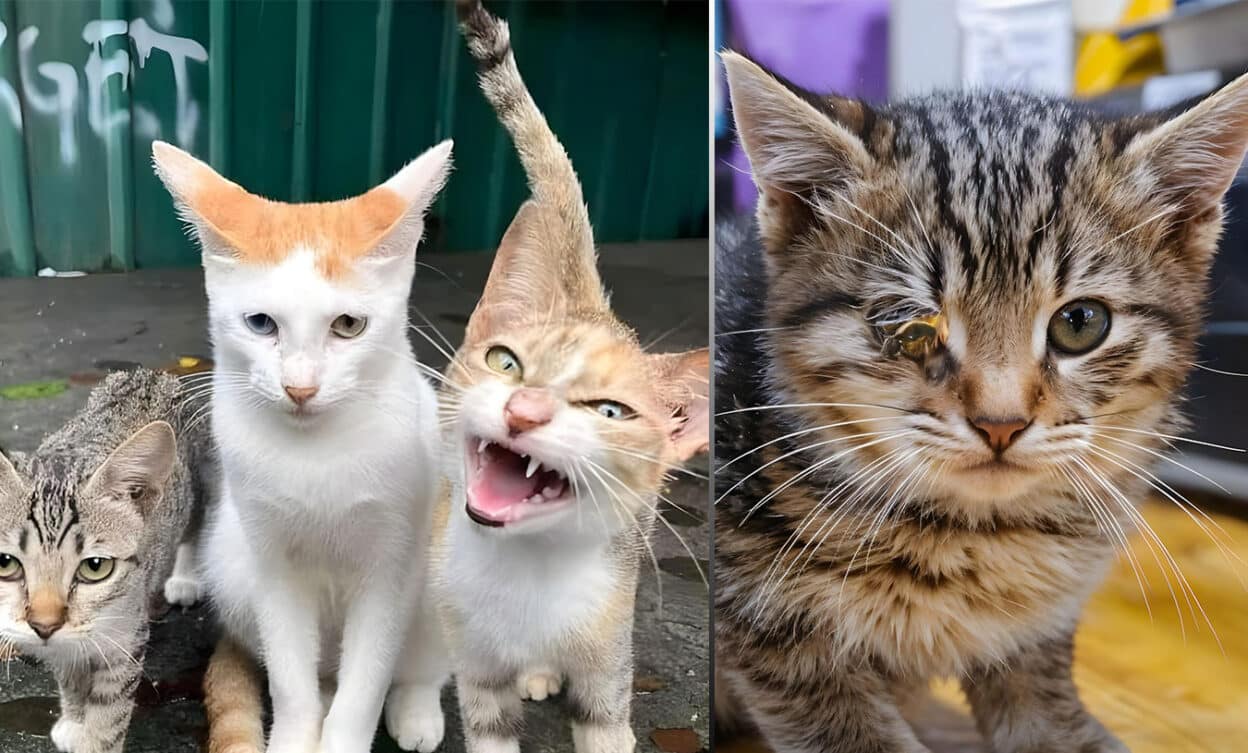
Stray cats often evoke a mix of emotions — compassion for their plight and caution about their potential health risks. In fact, their survival instincts are admirable, stray cats may carry diseases that pose significant risks to both humans and other animals. However, once you learn about these stray cat diseases and their effects, you may hesitate to approach them.
Understanding the Risks of Stray Cat Diseases
Stray cats face challenging living conditions that make them vulnerable to various infections and illnesses. Similarly, these diseases are not only dangerous to the cats themselves but can also be transmitted to humans and other pets. Let’s explore the most concerning risks.

Zoonotic Stray Cat Diseases
Zoonotic diseases are illnesses that can transfer from animals to humans. Indeed, stray cats are common carriers of these diseases due to their exposure to unsanitary environments and lack of medical care. Key zoonotic diseases include:
- Toxoplasmosis: Caused by a parasite found in cat feces, this disease can lead to severe complications in pregnant women and individuals with weak immune systems.
- Cat Scratch Fever: Spread by bacteria from a cat’s scratch or bite, this illness causes fever, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue.

Feline Infections and Risks
Stray cats are often exposed to harsh environments that increase their susceptibility to infections. These include:
- Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV): This virus weakens a cat’s immune system, making them vulnerable to other diseases.
- Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV): Similar to HIV in humans, FIV affects a cat’s immune response, leading to chronic infections.
These infections are highly contagious among cats, especially in areas with dense stray populations.
How Stray Cat Diseases Affect Humans and Other Pets
Diseases carried by stray cats don’t just endanger the cats themselves. Moreover, humans and pets that interact with infected strays are at risk of contracting illnesses. Here are some critical points to consider:
Parasites in Stray Cat
Stray cats often harbor parasites that can cause severe health problems:
- Fleas and Ticks: These parasites can transmit diseases like Lyme disease and bartonellosis.
- Roundworms and Hookworms: These intestinal parasites can infect humans. Especially children who come into contact with contaminated soil or surfaces.

Public Health and Stray Cats
Unvaccinated and untreated stray cats contribute to public health risks. Large populations of stray cats can:
- Spread zoonotic diseases more widely.
- Affect local ecosystems by hunting birds and small mammals.
Communities must address these risks of stray cat diseases through education and proactive measures.
How to Protect Yourself and Others
Awareness is the first step in protecting yourself from diseases carried by stray cats. However, here are practical ways to stay safe:
Avoid Direct Contact
- Avoid petting or handling stray cats unless absolutely necessary.
- Wear gloves and wash your hands thoroughly after any contact.

Seek Veterinary Care for Strays
If you decide to help a stray cat, ensure they receive a full health check from a veterinarian. Vaccinations and treatments can reduce health risks significantly.
Educate Others on Risks
Share information about the stray cat diseases that they can carry and the importance of safe handling. Encourage community programs for sterilization and vaccination of strays.
Final Thoughts
While stray cats deserve compassion and care, it’s essential to understand the potential risks they pose. It include a range of illnesses that can impact humans, pets, and other animals. However, by taking precautions and supporting community efforts to manage stray populations, we can ensure a healthier coexistence for all.
Have you encountered stray cats in your area? Share your experiences in the comments and let’s discuss ways to help these animals while keeping ourselves safe.